Tomorrow, Ferdinand “Bongbong” Marcos Jr. becomes the 17th president of the Republic of the Philippines.
Many of the so-called Marcos loyalists are, of course, ecstatic. Two of them, businessperson Serafia “Cherry” Cobarrubias and broadcaster/writer Rita Gadi, shared their joy—and pro-Marcos propaganda—on the livestreamed program of the latter, The Rita Gadi Hour, a few weeks after the May 9 elections.
Cobarrubias, who reportedly helped fund the December 1989 coup attempt against Corazon Aquino, insisted that Bongbong’s win was a miracle; that “the voice of God is the voice of the people”; and that members of the clergy who spoke against Bongbong should be ashamed of themselves and ask for forgiveness. Gadi, Marcos regime propagandist, insisted that there is no evidence that Marcos Sr.’s wealth came from the state’s coffers. Near the end of the livestream, Cobarrubias claimed that the former dictator, on his deathbed, said that only 3% of his wealth would be kept for his family and the rest of his assets worldwide “should go to the Filipino people.”
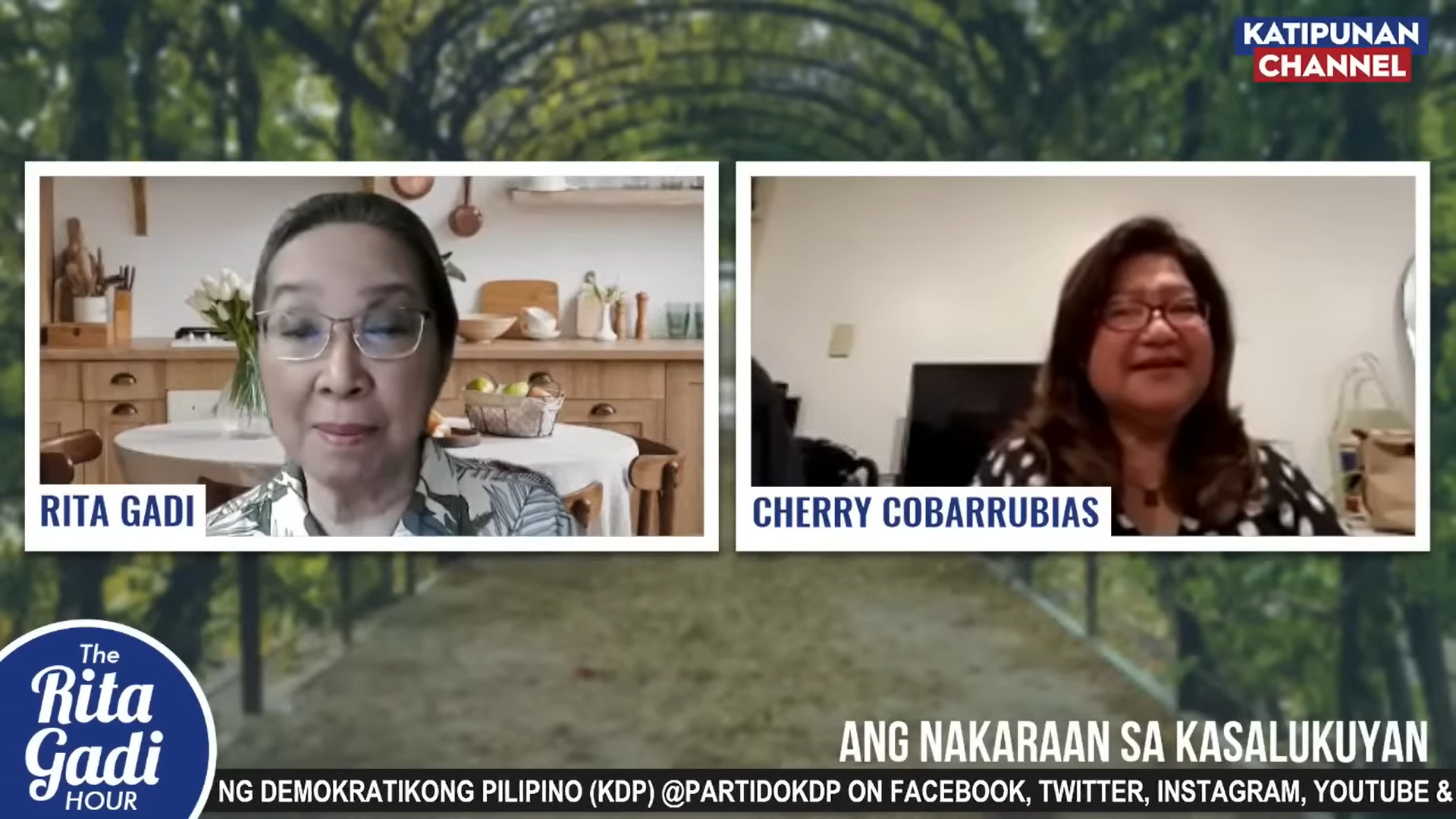
It seems safe to say, at least based on social media, that some who voted for Bongbong did so based on these claims, including the narrative that the family’s wealth would be used for the benefit of the entire country should a Marcos reoccupy Malacañang. Many loyalists believe that promise that was often repeated by Bongbong’s mother, Imelda.
Documents, however, show that Marcos Sr. himself never made such a pledge. At best, he set up the Ferdinand E. Marcos Foundation (FEMF) that did appear to serve a charitable purpose, in contrast to several other Marcos “foundations” that clearly functioned to help the family retain wealth that is far beyond what they could have legally earned. Ambiguous claims regarding FEMF’s funding sources and purpose became a basis for the Marcos family’s improbable vow to share their wealth. Such distortion of the truth then mutated into the scams that further propagated the myth of bounty for loyalty to the Marcoses.
The Ferdinand E. Marcos Foundation
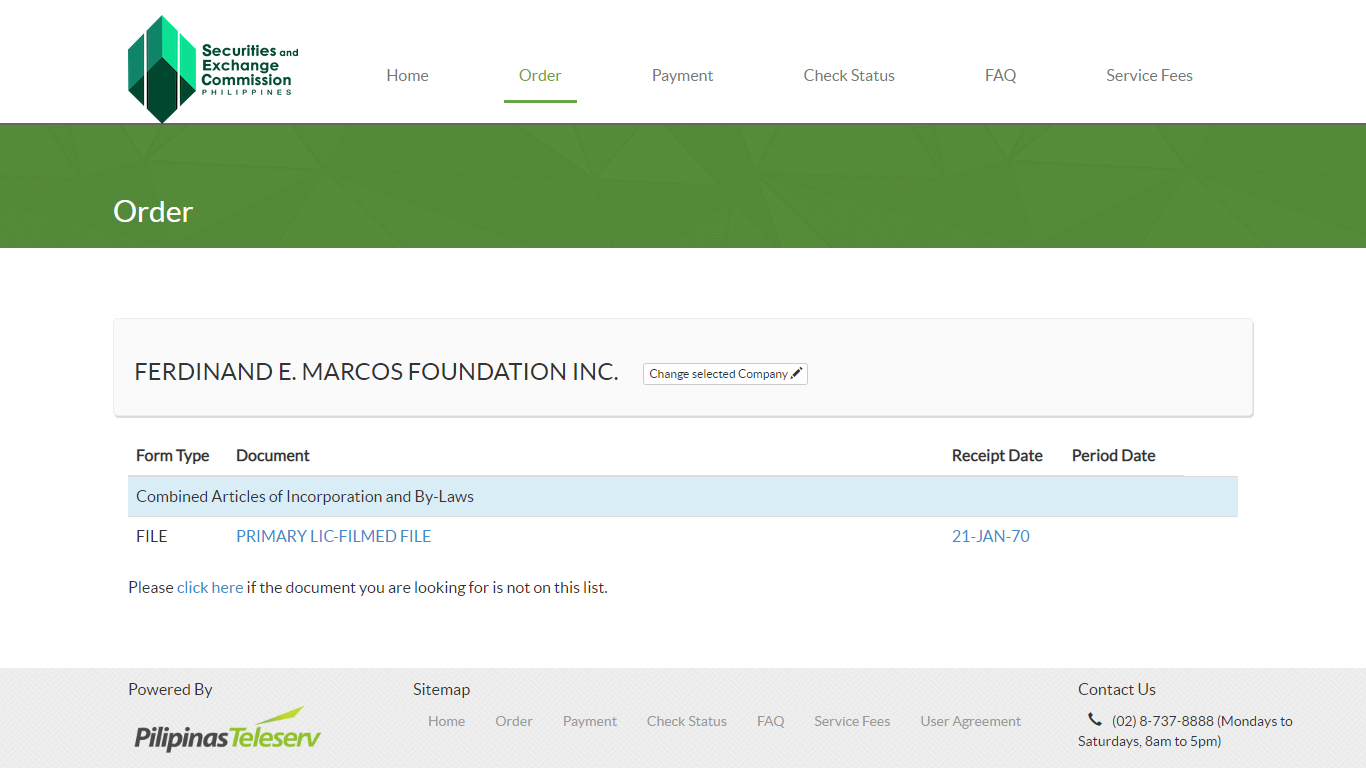
In 1970, at the start of his second term as president, Marcos Sr. publicly announced that he was putting all of his wealth in a foundation bearing his name. In a statement, the chief executive said he was motivated by “the strongest desire and the purest will to set the example of self-denial and self-sacrifice for all [his] people.” Records of the Security and Exchange Commission show that FEMF filed its articles of incorporation and by-laws on January 21, 1970, but in her book Marcos Martial Law: Never Again, author Raissa Robles said that the foundation’ registration had already been revoked by 2015.
Marcos Sr.’s announcement made headlines even in foreign media, quoting his statement. A wire story published in the Miami Herald mentioned that in 1968, “Marcos was listed for the first time among the Philippines’ top 100 income taxpayers” with the equivalent of over $160,000 “mostly from legal fees earned before he became president in 1965” even though his annual salary” was only $15,000. A 2003 decision written by former chief justice Renato Corona noted that Marcos Sr.’s income tax return just before becoming president “did not show any receivables from client at all” and there were “no documents showing any withholding tax certificates.”
A Manila Bulletin article discussed in the Philippine Weekly Economic Review noted that Marcos Sr.’s “properties, savings and investments [were to] go to the people through a foundation which will be used to advance education, science, technology and the arts,” but “did not specify” which assets or if these included conjugal properties with Imelda. In his 1970 statement and other speeches, Marcos only said that “[provisions] will be made for [his] children, so that they shall be assured of satisfactory education and be prepared to meet their lifetime duties and endeavors.”
The first couple poured millions of dollars into their children’s education, money that courts have ruled could not have been legally obtained. Expenditures included tuition, allowances, housing, and donations. Neither of the two Marcos children, Imee and Bongbong, who studied in universities abroad obtained scholarships. Both returned home without a degree.
After Marcos was deposed in 1986, it became clear that besides the money spent on their children’s education, properties purchased abroad, deposits made in U.S. banks as early as 1968, funds in Swiss bank accounts determined to be illegally obtained, among others, were not among the assets of the FEMF. To reiterate, Marcos never stated outright that his countrymen would have a redeemable share in the wealth he purportedly donated to the Foundation.
The FEMF had its headquarters in the Goldenberg Mansion on 838 Gen Solano Street, San Miguel, Manila which was christened with the name “Ang Maharlika.” In a 1979 speech, Marcos Sr. said the mansion was “bought by the Marcos Foundation and converted into a guest house and then donated to the government,” but the property was listed in the 1979 Philippine Yearbook as the site of the Marcos Foundation Museum.
The Sandiganbayan declared in a partial summary judgment on December 19, 2019 that paintings found at the Goldenberg mansion were ill-gotten and were forfeited in favor of the government. It noted that the Marcos heirs admitted owning the paintings in the mansion and other locations that were valued at $23 million, more than the legitimate income of the Marcoses before they fled the country. A particular set of paintings by American artist Grandma Moses displayed at the Goldenberg Mansion was, according to a New York Times article, collectively purchased for more than $600,000, about twice the Court-declared legal earnings of Marcos Sr. and his wife in their last term in office.
A list of science foundations certified by the National Science Development board as of January 30, 1972 included the FEMF, which was described as a funder of “research studies on behavioral and social sciences and the humanities; scholarships; professorial chairs; publication and dissemination of results of research studies.” Perhaps its best known project was the UP Los Baños’s National Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology for which FEMF committed P20 million for the purchase of laboratory furniture. A Supreme Court decision in 2004, however, pointed out that FEMF stopped paying the furniture supplier in early 1985 and its almost P1 million collectibles remained unpaid even after the fall of Marcos.
It appears that money from the Foundation was used for military research as well, although this is difficult to prove. An article published in April 1972 in the Far Eastern Economic Review mentioned that funding for the infamous Filipino-made missiles, one of which was nicknamed Bongbong, came “from the Marcos Foundation which the president said he would set up as his contribution to social amelioration.” It is unclear why no further progress was made in the local missile program beyond the first half of 1972.
Numerous government and non-state sources attest to the existence of FEMF-funded scholarships, but the number of scholars who benefitted from them appear to have been few. A Ministry of Education and Culture memorandum from April 1982 states that the Pangulo Scholarship Program was constituted by the Kabataang Barangay Foundation, Inc., and the FEMF in Oct. 1981. For the school year 1982-83, the program had 150 slots distributed in 13 regions. Pangulo scholars had to take one of five courses in six universities with “a monthly living yearly allowance of P5,000, excluding tuition and book allowance. In the 1986-87 academic year, slots for the Pangulo Scholarship slots were unlimited but students had to be active members of the Kabataang Barangay.
The name “Marcos Foundation” were in the copyright pages of numerous books purportedly written by Marcos Sr., many of which were distributed free. Studies have provided evidence that these books were in fact produced by ghostwriters and that at times, the money spent to publish came from government offers, not the FEMF. A statement of transactions in the files of the Presidential Commission on Good Government shows that the Foundation owed $31,120 to Prentice-Hall, Inc., publisher of “Marcos’s” book The Democratic Revolution in the Philippines, as of December 31, 1974.

The Foundation also attempted to fund a professorial chair at Tufts University’s Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy. Based on the February 1977 Official Month in Review published in the Official Gazette, the proposal to set up the chair was submitted to Marcos by Nihal W. Goonewardene, director of the Asia Pacific teaching fellowship program of Fletcher School based in Manila.” As reported by the Harvard Crimson, the FEMF had donated $500,000 to Tufts by January 1981 to establish the Ferdinand E. Marcos Chair for East Asian and Pacific Studies, and partly finance the construction of a school building. That same month, however, Marcos canceled the funding without withdrawing what had already been donated. Various explanations for this were given, but it was reported that numerous scholars declined the offer to fill the chair.
Lastly, the Foundation is also on record as a donor to at least one hospital and one university other than UP. These are the Mariano Marcos Memorial Hospital and Medical Center and the Mariano Marcos State University both name after Marcos Sr.’s father in Batac, Ilocos Norte.
From these snippets, it is quite clear that the Foundation was well endowed, but there was no indication that it had sufficient assets to make every Filipino wealthy or significantly address the country’s economic deficits; it certainly did not help in paying the country’s foreign debt. Moreover, the known assets of the Foundation were dwarfed by the billions of dollars in the Marcoses’ ill-gotten assets kept separate from what the FEMF managed.
Ferdinand Marcos’s Last Will and Testament
Not long after the EDSA Revolution, the PCGG focused on Marcos assets that were stashed abroad, in foundations that had the Marcoses as beneficiaries, or those kept for Marcos by dummies, some of which were recovered via compromise agreements. Based on the various versions of his last will and testament from 1980 to 1988, Marcos Sr. never had any other specified heirs besides his wife and children.
A portion of Marcos Sr.’s will from March 1982 was shown to journalists by his family in November 2016 to show what their patriarch said about his funeral and burial arrangements.
The PCGG has the full version of the will in its files and among the appendices of the book Marcos Legacy Revisited: Raiders of the Lost Gold by Erick San Juan, published in 1998. The portion not shown to the media contained details of his wealth that Marcos Sr. bequeathed entirely to his wife and their three children and adopted daughter Aimee. The FEMF is mentioned only as an executor in case of his wife’s “default or incapacity.” The will also contained this provision: “I hereby revoke any and all my other wills, codicils, or testamentary dispositions heretofore executed, signed, or published, or alleged to have been executed, signed, or published by me.”
If Marcos ever willed any of his assets to go to other people other than his only son and wife after his death prior to March 1982, he had effectively withdrawn it.

That revocation clause (a standard feature of wills) was retained in another version of his will, made a month later. This one too appears in San Juan’s book and kept in PCGG’s files. The most glaring alteration in this version is the removal of the Marcos Foundation as secondary executor and in its place, Bongbong was designated as executor along with Imelda.
A 1988 version of Marcos’s will has been published at least twice: in the October 7, 1992 issue of the Manila Standard, which noted that the document had been “acknowledged” by Imelda, according to former senator Rene Saguisag; and in San Juan’s Raiders of the Lost Gold. Substantively,the will remained similar to its earlier incarnation, again naming Bongbong and Imelda as co-executors. Bongbong’s name was dropped in 1982 and reinstated in 1988. The 1988 will, or a later version of it, appears to have been Marcos Sr.’s last.

Ferdinand Sr. died on September 28, 1989. Despite the government’s attempts to disqualify them from performing their duties, the Supreme Court, in Republic v. Marcos II, affirmed that Bongbong and Imelda were the co-executors of Marcos Jr.’s will but this did not give either of them a say on what to do with the billions recovered by the PCGG.
False Promises and Compromises
Not long after her husband’s death, Imelda began saying that she would use all of her family’s wealth for the benefit of the nation as supposedly intended by Marcos Sr. She said it in 1990 after she was acquitted of violating the U. S. Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act, mail fraud, and obstruction of justice and a year later, in a press conference on her return from exile. Imelda said she had wanted to release some of their money to support “typhoon victims, for earthquake victims, for [those affected by the eruption of Mt.] Pinatubo” but that “was not allowed.”
There is no known evidence to support this.
By that time, over five years had passed since the Swiss government had frozen the Marcos bank accounts in Switzerland after an attempted withdrawal of $200 million in deposits in March 1986, when the Marcoses were already in exile. When Imelda returned to the country, a settlement had been made in which the government would drop a civil racketeering case against the former first lady “in California and all other pending or future suits against her in U.S. courts in return for an estimated $8 million worth of Marcos property” in that country, the Washington Post had reported.
The settlement did not include the dropping of lawsuits filed by private individuals, some of which were successful.
By saying at that time that they needed permission to access funds for disaster relief, Imelda was practically stating that beyond what was discovered by various governments, the Marcoses had relatively little else. Indeed, even the P27 million in freshly minted bank notes that they “unintentionally exported” to Hawaii when they landed there in February 1986 were seized from them and partly returned to the Philippine government, already demonetized, in 1992.
Perhaps this was why she did not make the distribution of her family’s wealth a highlight in her 1992 presidential campaign. Her 15-point platform did not mention it, but some of her most important loyalists did it for her. Among them was writer/educator Reynaldo T. Fajardo, a founding member of the organizationFriends of Imelda Romualdez Marcos or FIRM, also known as FIRM-24K.
Fajardo wrote a number of pro-Marcos books in the late 1980s and the 1990s, including The Acquittal, Homecoming, and Inevitable Rise to the Presidency of Imelda Romualdez Marcos, published in 1991. In his book, Fajardo claimed that Marcos Sr. “wanted to use [his] stupendous wealth [purportedly hundreds of billions worth of gold] to turn the Philippines into a self-reliant and truly sovereign nation that would gain the respect of the rest of the world.” He added that in fact, Marcos Sr. “said that he was also sympathetic with the miserable plight of the other underdeveloped and developing countries” and “planned to help them, too.”
One can’t help but wonder why the former dictator did not do that when he was president.
Fajardo also said the “vast wealth that the late President accumulated and conserved” was intended to be used “to accomplish his vision for the country,” and that Imelda would “use effectively” this wealth “left with her by the President.”

Imelda would later echo this as a campaign promise. An article published in March 1998 in the Manila Standard with the headline “Imelda Reveals more Secret Bank Accounts,” stated that the Marcos widow, then a presidential candidate, claimed that her family had over $800 million “in secret bank accounts abroad that she would give to the poor Filipinos if she wins the May presidential election.” That amount supposedly excluded funds that were previously identified as ill-gotten in Swiss bank accounts. Imelda said that even she was “not aware of the extent of [their] wealth,” further claiming that her husband’s money was a product of “diligence, hard work, foresight, entrepreneurship and God’s blessing.”
The Standard reported that Imelda showed the press a photocopy of a purported handwritten will of Marcos Sr. stating that “his worldly goods have been placed in the custody and for the disposition of the Marcos foundations [sic] dedicated to the welfare of the Filipino people.” Another article, published in Sol Jose Vanzi’s Philippine Headline News Online on April 15, 2004, dates this alleged “handwritten legacy” as being executed on April 9, 1973.
If true, then the wills Marcos executed in the 1980 leaving all of his wealth to members of his immediate family, superseded the 1973 one.
Still, Imelda insisted her husband wanted to leave all his wealth to the people. In December 1998, months after she withdrew from the presidential race to support the eventual winner, Joseph Estrada, Imelda testified during a senate hearing that she wanted the chamber’s help to “implement the last will and testament of the late President Marcos, to enlist assets in the hands of trustees, to implement the Marcos Humanitarian Foundation, so that we can help the country in our economic crisis and help the Filipino people in their agony and suffering.”
Imelda made the appeal after claiming in a series of articles published in the Philippine Daily Inquirer that her family “practically [owned] everything in the Philippines.” During her 70th birthday a year later, before a cheering crowd in a church, she declared in Filipino that she was convinced Estrada would find a way to settle with the Marcoses and this would lead to the establishment of a Marcos Foundation to help the country.
In 2004, she and her children threw their support behind presidential candidate (and Estrada ally) Fernando Poe Jr., because, as per Imelda, “FPJ [will help implement] the last will of Ferdinand Marcos, which is to help the people even if he [Marcos] is already gone.” According to an April 2004 Philippine Daily Inquirer article, Imelda said “that if Poe won, the Marcoses would willingly give [their assets] to the government so he could use it for the people.”
Over time, Imelda’s claims became wilder becoming not only about distributing money, but also promising a stake for Filipinos in the fictitious deuterium deposits in the Philippine Deep.
These did not exactly jibe with statement made not only by her husband when was still alive but also those made by Bongbong, especially when the family wanted to make compromise agreements with the government. Before the Marcos patriarch died, according to various news accounts, the family, through alleged intermediaries, offered to give anywhere between $2.1 billion to $5 billion to the government so they could return to the Philippines. Former vice president Salvador Laurel maintained that the elder Marcos was willing to give 90% of his wealth which could have left the family $550 million.
But Marcos Sr. was a notoriously unreliable source regarding his wealth. In 1987, he was still outrightly denying that he had any Swiss bank accounts or hidden wealth. In the same year, in the infamous “Marcos Tapes” in which the exiled dictator was secretly recorded talking about a plan to invade the Philippines, Marcos Sr. mentioned that he had billions of U.S. dollars worth of gold, and that Bongbong knew where part of that hoard was. During a hearing on the Marcos tapes at the Subcommittee on Asian and Pacific Affairs of the U.S. House of Representatives, Representative Jim Leach said that the Marcos gold, “while representing a monstrous theft, cannot possibly be of such monumental proportions.”
For his part, Bongbong has repeatedly asserted that his father made his money partly by trading in precious metals although this has never been judicially acknowledged in the Philippines. More importantly, Bongbong deviated from his mother’s claims by insisting that compromising or sharing their wealth with the government was not a means to fulfill some philanthropic final wish of his father but a way for their family to be rid of their remaining cases in one fell swoop.
A November 2, 1997 article published in the Filipino Express stated that Bongbong, then on hiatus from politics after failing to win a senate seat in 1995, wanted to compromise only to give his family immunity. That was the whole point, he stated; “Kaya namin ginagawa ito para malinis na ang lahat, mawala na ang kaso, maayos na ang hatian sa alleged Marcos assets.” He also insisted that there was no more hidden wealth beyond what had already been identified in the frozen Swiss bank accounts. If anyone could find more, it’s theirs, he effectively said.
An earlier settlement try in 1993 was junked by the Philippine Supreme Court for several reasons, including the impossibility of granting the Marcoses immunity (since they were the principal defendants in numerous cases and would not stand as witness against other defendants) and the fact that then president, Fidel Ramos was not a signatory to the agreement between PCGG and the Marcoses.
By 1997, Ramos, with support from the majority of the senate, asked Congress for a law allowing him to enter into a compromise with the Marcoses following a proposal from Bongbong, according to an October 1997 South China Morning Post article. While the senate, based on a Manila Standard article published that same month, was willing to do that or provide, in the words of the late senator Miriam Defensor Santiago, a (limited) special power of attorney, it did not happen.
Soon after Estrada became president, he reiterated his campaign trail declaration that he wanted to give executive clemency to Imelda, but as reported in a January 1999 Xinhua News Agency article, the family must have a united voice. Perhaps Estrada noted the disconnect between Imelda’s claims of unfathomable wealth for the people and Bongbong’s more pragmatic stance. He was mainly talking to Bongbong and no agreement was reached.
Bongbong made it seem that it was only through a compromise that the government could get its hands on the Swiss funds, but a condition for the transfer of the money was a final judgment of conviction on the Marcoses. By the early 2000s, this had not been met technically but all that was really necessary for the transfer was the 2003 Supreme Court decision, written by Chief Justice Corona, declaring the wealth in excess of the Marcoses’ legitimate income as ill-gotten. By then, the funds had reached over $650 million.
The Basis of Loyalist Loyalty?
While Bongbong’s ultimately unsuccessful attempts to reach a compromise with the government appealed to decision makers, especially those frustrated with a supposedly underperforming PCGG and the Marcoses’ legal maneuverings, it was Imelda’s more fantastic claims that drew many die-hard loyalists to the family’s side. FIRM 24-K would hold on to Imelda’s promise of wealth distribution even through the last decade, when their president, Artemio Lachica, claimed that the share of its members in the Marcos wealth would only be given once the Marcoses get what they are fighting for. Apparently, some FIRM 24-K’s members were promised a million pesos for participating in the organization’s tree-planting program where they had to pay for the seedlings, according to a 2022 article published in the Philippine Star after the elections.
There are other groups like FIRM 24-K. In a November 2017 Facebook post, popular pro-Marcos vlogger Maharlika said she was not connected to what she labeled a scammer group, Maharlika Marcos Loyalist, Inc., which, like FIRM 24-K, collected fees while promising to give money or wealth. Photo/video evidence show that this group, Inc. was among the organizers of Imelda’s ill-fated 90th birthday celebration in July 2019 at the Ynares Stadium in Pasig where hundreds suffered food poisoning.
Both groups are recognized by the Marcoses. One of FIRM 24-K’s Facebook pages uploaded two videos showing that they can legitimately claim to have pushed Bongbong to run for national office again in the 2010 elections where he won a seat in the Senate, and another one that had Imelda pledging a P1 million seed fund to its “Anima Foundation.” Such Marcos-sanctioned groups have spun off into other organizations claiming to help give people a stake in the Marcos wealth but whose direct ties to the family, if any, are not readily apparent. An example is the scammer group Bullion Buyer Ltd., which organized an event in 2017 where thousands flocked to UP Los Baños to claim—unsuccessfully—a few thousand pesos allegedly from the Marcos’s coffers.

It is difficult to ascertain how many voted for Bongbong with the belief that he would pave the way for mass wealth distribution. Based on Google Trends, there was a spike in search interest on the late dictator’s last will and testament days after Bongbong’s win became a certainty. FIRM 24-K alone claims millions of members nationwide. The program at the UPLB event claimed that Bullion Buyer Ltd. already had over 281,000 beneficiaries. And no matter how many times these are debunked, sometimes by the Marcoses themselves, claims that the family would give away either a share in their “Tallano gold” or help people monetize their claims to “deuterium deposits” under a Bongbong Marcos presidency remain popular.
But what if this does not happen?
In 2002, according to a November 10 Inquirer article, several long-time loyalists claimed that they were severing ties with the Marcos widow — and preparing a book that would show the “real Imelda”— after it was said that she had settled with the Cojuangcos on the ownership of the Philippine Long Distance Telephone Co. for a staggering P2 billion. Among these loyalists were surprisingly, Cobarrubias, and Gadi. Their gripe? Imelda was, as mentioned by a loyalist, “in a position and has the means to fulfill” her promise of “setting up a Marcos foundation to benefit the poor.”
Gadi was quoted by the Inquirer as saying that Imelda was “in a position to help her loyalists, but I see no sign on her part.” Things were so bad between Imelda and her former “groupies,” as a November 2002 Arab News article called them, that they started calling Imelda a liar, or “a master of acting and deception.” They were still angry at Imelda a year later, with no indication that the incredibly wealthy Antonio Vialogo, who funded Imelda’s 70th birthday bash in 1999, would throw another birthday party for the former first lady again.

But in the year before Bongbong became a senator, Imelda reconciled with Cobarrubias and company. All of them became the staunchest of Marcos supporters again, and their tell-all anti-Imelda book did not materialize. According to a Rappler report, Oscar Violago, Anthony’s father, contributed P15 million to Imee’s successful senate campaign in 2019. Cobarrubias, during her recent guesting in Gadi’s online program, happily talked about funding the production and publication of the pro-Marcos books of the Katarungan at Katotohanan (Truth and Justice) Foundation, Inc., such as Hubris: When States and Men Dare God – The Persecution of the Marcoses.
For some, money probably does help fuel loyalty to the Marcoses. Marcos “inheritance” or “biyaya/ayuda” scams persist to this day. Some are relatively unsophisticated, such as a recently debunked claim circulating online after the elections that Bongbong was giving aid in exchange for personal information. Others are utterly bizarre, such as at least two recent videos, with hundreds of thousands of views on YouTube alone, claiming that Marcos Sr. is still alive, and that the man himself, and not Bongbong, would bring prosperity to all.
Even Cobarrubias, in conversation with Gadi, said that the former president metaphorically rose from the dead (“bumangon tuloy si Ser”) and campaigned in the last election. Indeed faith, partly disinformation-driven, in a dead man who supposedly gave up his wealth for his people—all evidence to the contrary— is probably also difficult to shake off for many who had already invested so much in the Marcos cause. Millions, scammed or otherwise, are probably ecstatic about the Second Coming of Ferdinand Marcos – Senior or Junior.
They helped put a Marcos back in Malacañang; will the Marcos heirs reward their faith?
(Miguel Paolo P. Reyes is a university research associate at the Third World Studies Center, College of Social Sciences and Philosophy, University of the Philippines Diliman. Joel F. Ariate Jr. and Larah Vinda Del Mundo helped in writing this article. This piece is part of their Center’s on-going research program, the Marcos Regime Research.)




